Note that in all lessons on GTR the strings are numbered in a different, more sensible way than most guitar instructors and resources teach: Numbering The Guitar Strings
A learning tool that has become quite popular over the past few years is the CAGED chord pattern. The guitar is set up and tuned in such a way that you can play chords in several positions all over the neck. This means that rather than just being able to play a C Major chord in one place on the fretboard you can learn to play it in 10 different positions (5 in each octave). Each chord position has its own feel which gives you a wider palette of sounds to choose from when playing. It is also a great tool to help you learn all the note names on the fretboard as well as the major scale.
As its name shows, the CAGED chord pattern is a pattern of 5 chord shapes. These are the C-shape, A-shape, G-shape, E-shape and D-shape. Have a look at the previous lesson to see what these chord shapes look like: Lesson 3: Basic Guitar Chords For Beginners.
Now this is the part that can be a bit confusing. In order to be able to use the CAGED chord pattern you need to learn the shapes of those 5 chords and for the moment separate them from the specific notes that are being played. So look at the chord diagrams for the chords C, A, G, E and D and pretend they are blank chord finger patterns. Memorise how you have to hold your fingers for each of those chords. How you hold your fingers for each chord is what we call its shape.
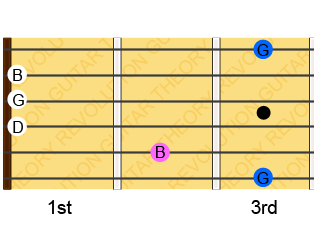
So lets say you want to find out what the other 4 positions of the C Major chord look like. To do that you map out all the notes that make up the C Major chord (C, E and G) as I’ve done below.

You should recognise the C Major chord on the left side of the image at the 1st, 2nd and 3rd frets. In this position you won’t normally play the two G’s on the 1st and 6th string but you could if you wanted to. That’s the C-shape of the C Major chord.
The next letter in the CAGED chord pattern is A which means the next C Major chord will have the A-shape. Can you see where the A-shape appears in the image? It’s at the 5th fret. The G-shape appears at the 7th and 8th fret, the E-shape at the 9th and 10th and the D-shape at the 12th and 13th fret (the notes at the 13th fret are the same as the 1st). So now you can play a C Major chord at 5 different places between the 1st and 12th fret (so 10 different places across the 2 octaves of a guitar fretboard).
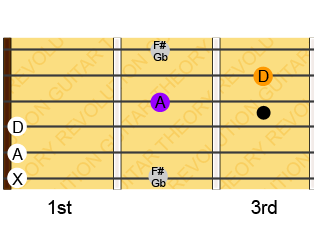
Lets look at what the CAGED pattern look like for the A Major chord (made from the notes A, C#/Db and E).

Again you should recognise the A Major chord on the left side of the image. The next letter in the CAGED pattern is the G-shape which you can see at the 4th and 5th fret, the E-shape at the 6th and 7th, the D-shape at the 9th and 10th and the C-shape between the 10th and 12th fret.
You can repeat this method for the other chords G, E and D. Just start with the chord in the open position (at the first 3 frets) then find the next shape by looking at which letter shape appears next in the word CAGED. BTW you can see in the A Major diagram above that the D shape links in with the C shape. This means that the pattern repeats endlessly CAGEDCAGEDCAGED etc.
So the order of shapes for these 5 chords is as follows, starting from the open position at the 1st to the 3rd fret.
CAGEDCAGED etc.
AGEDCAGEDC etc.
GEDCAGEDCA etc.
EDCAGEDCAG etc.
DCAGEDCAGE etc.
I’d advise you to concentrate on learning the pattern for these five chords until you have a good feel for where they are in relation to each other. It won’t take long until you can find all the chord positions for each chord without thinking about it.
The CAGED pattern doesn’t just apply to the chords C, A, G, E and D. It holds for all major chords, F#, A# and Eb for example. Just take a look at the image below which shows all the notes for the F# Major chord (the notes F#/Gb, A#/Bb and C#/Db). You can easily spot the CAGED pattern shapes on the fretboard.
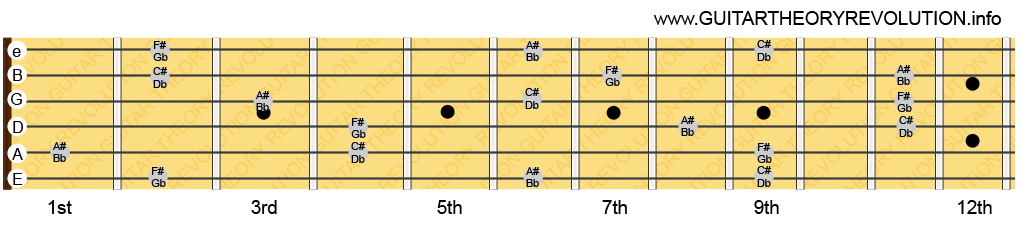
The E-shape appears at the 3rd and 4th fret, the D-shape at the 6th and 7th, the C-shape between the 7th and 9th and the A-shape at the 11th fret.
Learning the CAGED chord pattern is a great way to gain insight into the fretboard and music theory. If you want a more in depth lesson on the CAGED pattern including more detailed diagrams I can send them to you when you sign up for the Guitar Theory Revolution Newsletter.